A109
Difference between revisions of "A109"
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The activities associated with the selection of the key metrics for each performance attribute for each supply chain. A scorecard is used to define the metrics of most interest to an organization, to arrange them by area of impact, by business priority, and to provide a container for later benchmarking comparisons. Each scorecard is built from a subset of hundreds of {{OR}} metrics. | The activities associated with the selection of the key metrics for each performance attribute for each supply chain. A scorecard is used to define the metrics of most interest to an organization, to arrange them by area of impact, by business priority, and to provide a container for later benchmarking comparisons. Each scorecard is built from a subset of hundreds of {{OR}} metrics. | ||
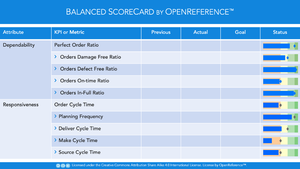
===Balanced Scorecards=== | ===Balanced Scorecards=== | ||
| − | [[File:OR-BSC.png|thumb|Balanced Scorecard | + | [[File:OR-BSC.png|thumb|Balanced Scorecard example]]A standard method to analyze the performance of supply chains is the use of [[t:BSC|Balanced Scorecards]]. A [[t:BSC]] consists of a limited number of agreed, well-defined metrics, categorized by business perspective. |
| − | |||
An example of such metrics are the level-1 [[SCPM|metrics]] for each [[Attribute|Attribute]] defined in {{OR}}. Where necessary the level-2, 3, and 4 metrics are available to analyze and explain deviations between scorecard targets and actuals for each metric. | An example of such metrics are the level-1 [[SCPM|metrics]] for each [[Attribute|Attribute]] defined in {{OR}}. Where necessary the level-2, 3, and 4 metrics are available to analyze and explain deviations between scorecard targets and actuals for each metric. | ||
Revision as of 16:16, 17 November 2021
The activities associated with the selection of the key metrics for each performance attribute for each supply chain. A scorecard is used to define the metrics of most interest to an organization, to arrange them by area of impact, by business priority, and to provide a container for later benchmarking comparisons. Each scorecard is built from a subset of hundreds of OpenReference metrics.
Balanced Scorecards
A standard method to analyze the performance of supply chains is the use of Balanced Scorecards. A Balanced Scorecard consists of a limited number of agreed, well-defined metrics, categorized by business perspective.An example of such metrics are the level-1 Metrics for each Performance Attribute defined in OpenReference. Where necessary the level-2, 3, and 4 metrics are available to analyze and explain deviations between scorecard targets and actuals for each metric.
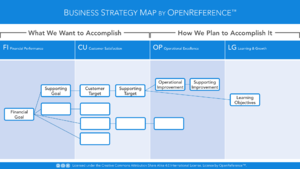
Business Strategy Maps
A Business Strategy MapNotes
Busines Plan Review is a key step prior to defining scorecards. Without a deep understanding of the business plan, metrics are typically not --clearly-- linked to business priorities. Developing the Business Strategy Map will reveal any gaps in linkage between priorities and metrics. The Discovery (A102) and Documentation/definition (A108) of supply chains are a key preceding steps. Without clearly defined supply chains, scorecards may contain aggregate data of conflicting supply chain types e.g. Make-to-Order and Make-to-Stock together.
Workflow
| Process |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A109 |
|
||||||||||||||||||